-
Photonics are Key!
Using state-of-the-art diode and fiber laser based technology, TOPTICA is a key enabler for quantum and biophotonics applications. TOPTICA will display their latest laser systems for scientific and industrial applications at Photonics West in San Francisco from January 25-27, booth #1227. Dedicated laser solutions for biophotonics will be shown at the BiOS Expo January 22-23, booth #8326. Here we present some of our highlights of this year’s Photonics West. More live demos can be expected at our booth. World leading efficiency ranging from deep UV to near infrared TOPTICA presents TA-SHG pro and TA-FHG pro – High-power, tunable, frequency-doubled or quadrupled diode laser @ 205 .. 780 nm, up to…
-
World leading efficiency ranging from deep UV to near infrared
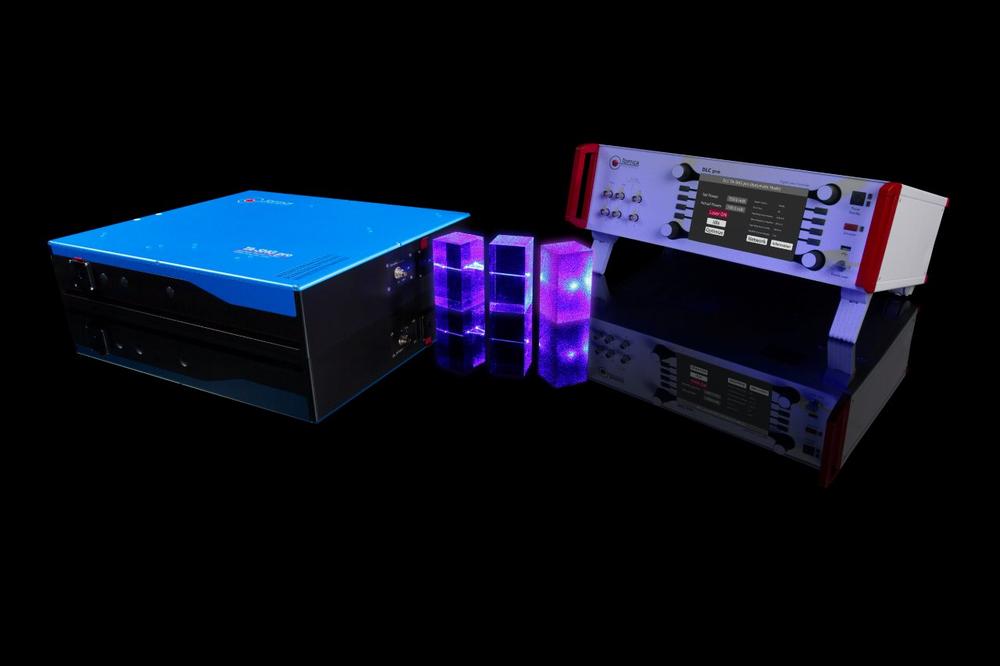
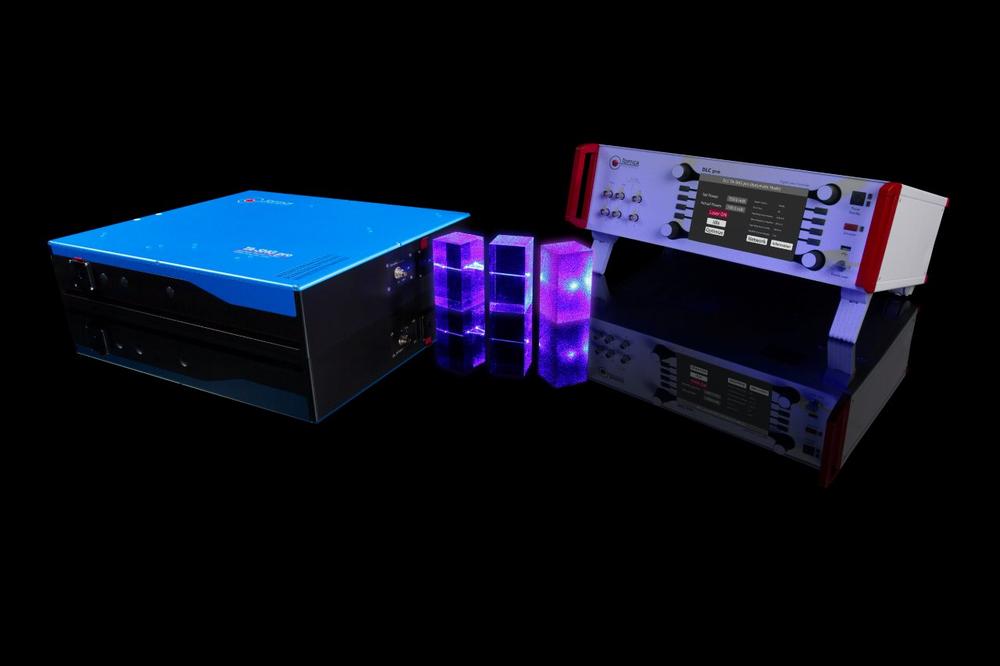
Nonlinear frequency conversion techniques access wavelengths that cannot be generated directly from laser diode technology. Via second or fourth harmonic generation, TOPTICA laser systems can access the UV, blue, green, yellow and orange spectral ranges at high powers. TA-SHG pro and TA-FHG pro – High-power, tunable, frequency-doubled or quadrupled diode laser The TA-SHG pro system, part of the UV / RGB solutions, comprises a tunable diode laser, a high power semiconductor (TA) and an integrated frequency doubling stage (SHG pro). Alternatively, it is available with a fiber (FA) or Raman fiber (RFA) amplifier. The SHG stage is a folded ring cavity in bow-tie configuration with excellent thermal and mechanical stability.…
-
Leistungssieger vom tiefen UV bis zum nahen Infrarot
Nichtlineare Frequenzkonversionstechniken ermöglichen Wellenlängen, die bislang mit der Laserdiodentechnologie nicht direkt generiert werden können. Durch Frequenzverdopplung oder Frequenzvervierfachung können TOPTICA Lasersysteme den UV-, Blau-, Grün-, Gelb- und Orange-Spektralbereich bei hohen Leistungen erreichen. TA-SHG pro und TA-FHG pro – Durchstimmbarer, frequenzverdoppelter oder -vervierfachter Diodenlaser mit hoher Leistung Das TA-SHG pro-System, Teil der UV/RGB-Lösungen, besteht aus einem abstimmbaren Diodenlaser, einem Hochleistungshalbleiter (TA) und einer integrierten Frequenzverdopplungsstufe (SHG pro). Alternativ ist es auch mit einem Faser- (FA) oder Raman-Faser- (RFA) Verstärker erhältlich. Die SHG-Stufe ist eine gefaltete Ringkavität in Bow-Tie-Konfiguration mit ausgezeichneter thermischer und mechanischer Stabilität. Das TA-FHG pro-System ist eine durchstimmbare, diodenbasierte Laserquelle im tiefen UV-Spektralbereich. Das System besteht aus einer zusätzlichen…
-
Trapped-ion quantum computers in Germany
TOPTICA is a proud partner in the project ATIQ that started this month. It is the largest German consortium to build, operate and use quantum-computing demonstrators based on trapped ions. 25 partners from industry, research institutions and academia have teamed up to tackle the related challenges and exploit the huge potential of quantum-computing technology, aiming for reliable and user-friendly 24/7 operation. The German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) funds 84.1% of this 44.5 million euro project. The quantum computers will rely heavily on TOPTICA technology. To this end, TOPTICA will perform research on advanced technologies tailored for the precise conditioning of laser light. The resulting prototypes will be…
-
Lasers for Neuroscience
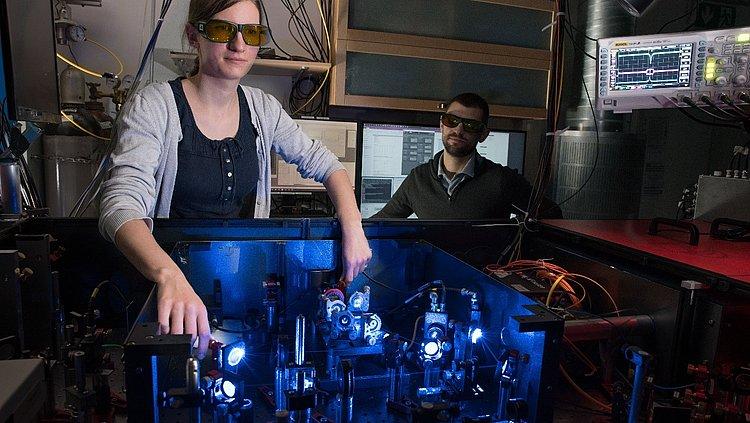
2-photon fluorescence microscopy has become a key technology in biological imaging in neuroscience enabling three-dimensional, noninvasive studies of the neuronal structure and activity on the submicron scale. The contrast mechanism in 2-photon microscopy in neuroscientific research is based on the excitation of green or red fluorescent proteins, so called GFPs and RFP, by two photons in the infrared spectral range. To drive this nonlinear process and to resolve the neurons deep within the living brain, femtosecond lasers with clean temporal pulse shape and average output powers of >1W are an essential prerequisite. Going beyond pure imaging, all-optical interrogation is a novel approach to understand how active patterns in neuronal activity…
-
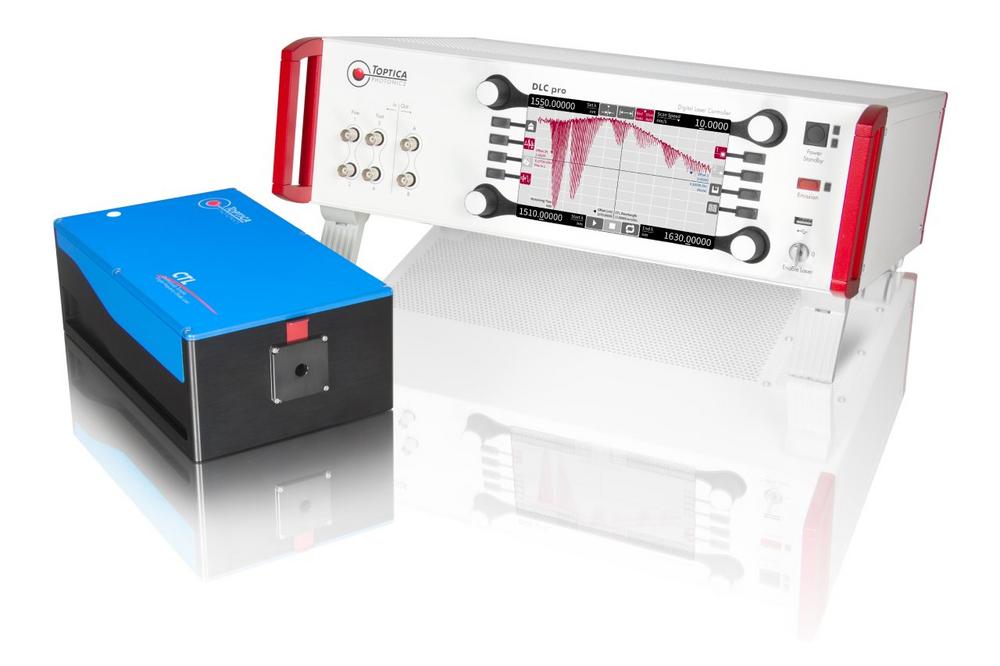
Messungen am Quantenlimit
Die Laser der CTL-Produktfamilie von TOPTICA sind ideale Werkzeuge für die Anregung von Mikroresonatoren oder Quantenpunkten, für das Pumpen von Mikrofrequenzkämmen sowie für die Komponentenprüfung und Spektroskopie. Ihre wichtigste Eigenschaft ist die breite und kontinuierliche Durchstimmbarkeit ohne Modensprünge. Sie bieten eine große Leistung, eine schmale Linienbreite und eine hohe Wellenlängenstabilität. Mit den CTL lassen sich Wellenlängenscans mit höchster Auflösung durchführen. Das einzigartige Zusammenspiel der vorgenannten Eigenschaften macht die CTL-Familie auf ihrem Gebiet herausragend und ermöglicht es Forschern, Messungen am Quantenlimit durchzuführen. Mit dem volldigitalen, rausch- und driftarmen DLC pro-Controller ist der Laser über Touchscreen und Drehknöpfe sowie per PC-Benutzeroberfläche und Befehlsschnittstelle (Python SDK) einfach zu bedienen und zu steuern. Mit…
-
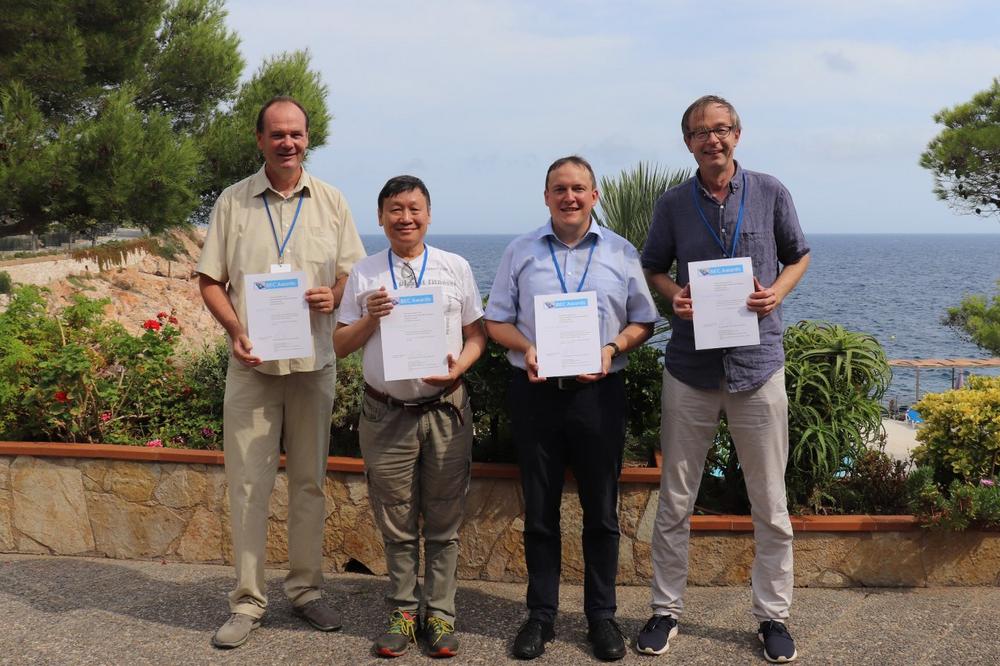
Bose-Einstein Condensation Awards 2021
The BEC Awards ceremony took place during this year’s conference Bose-Einstein Condensation (BEC) 2021. The winners of the TOPTICA BEC Awards are elected biannually by an independent scientific committee. The TOPTICA Senior and Junior BEC Awards honor outstanding research in Experimental and/or Theoretical Physics of Quantum Degenerate Atomic Gases. The newly established TOPTICA BEC Award for Lifetime Achievements recognizes longstanding important contributions to the field. Dr. Juergen Stuhler, Vice President Quantum Technologies at TOPTICA, handed over the awards in Sant Feliu de Guixols (Spain) on 12th of September 2021. “TOPTICA is proud to sponsor the recognized awards in a research field that developed symbiotically together with our company over the…
-
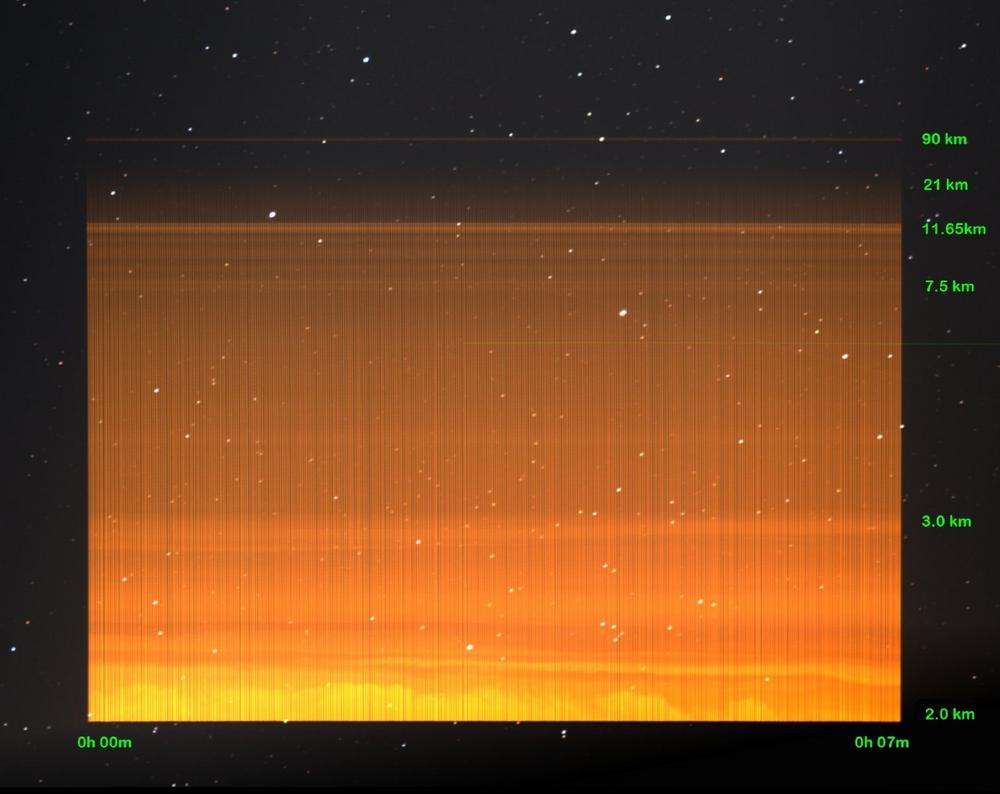
International Day for the Preservation of the Ozone Layer
Today is the International Day for the Preservation of the Ozone Layer. The ozone layer protects life on Earth from harmful solar ultraviolet (UV) radiation. The ozone layer is located 50 kilometers above the earth’s surface. It forms the transition to space and is part of the stratosphere. This is located at an altitude of about 15 to 50 kilometers and contains 90 percent of atmospheric ozone. The sun’s high-energy ultraviolet radiation (UV-C) converts oxygen (O2) into ozone (O3) there. Ozone is nowadays measured optically with (UV) lasers, from Earth and from satellites. Fast up- and downloading high volumes of data from these satellites in the future will need again…
-
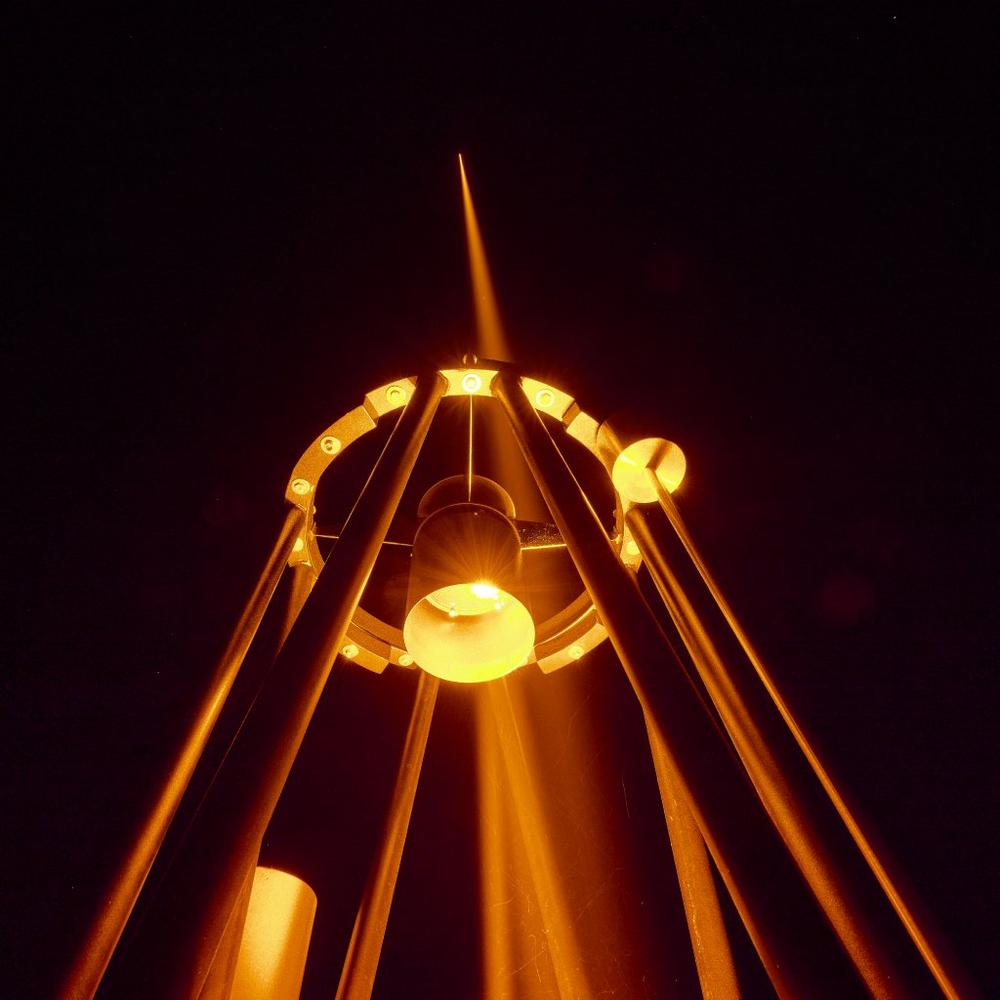
Leistungsstärkerer Laserleitstern besteht ersten Feldtest am Teleskop
Das adaptiv-optische Lasersystem verfügt im Vergleich zu bestehenden Systemen über wichtige zusätzliche Fähigkeiten. Er soll an der optischen Bodenstation der Europäischen Weltraumorganisation (ESA) auf Teneriffa, Spanien, im Rahmen der Forschungs- und Entwicklungszusammenarbeit zwischen ESO und ESA installiert werden. Die höhere Laserleistung und das neuartige Chirping-System werden die Schärfe astronomischer Bilder, die mit bodengebundenen Teleskopen aufgenommen werden, erheblich verbessern. Die Technologie öffnet auch die Tür für Entwicklungen in der Laser-Satellitenkommunikation. Die adaptive Optik in der Astronomie bezieht sich auf Systeme bei bodengebundenen Teleskopen, die den durch Turbulenzen in der Erdatmosphäre verursachten Unschärfeeffekt korrigieren – den gleichen Effekt, der die von der Erde aus gesehenen Sterne zum "Glitzern" bringt. Um die Verzerrungen…
-
New powerful laser passes field test
A powerful experimental laser developed by the European Southern Observatory (ESO), TOPTICA Projects1 and other industry partners2 passed a key test last month at the Allgaeuer Volkssternwarte Ottobeuren observatory in Germany. The adaptive-optics laser has important additional capabilities compared to existing systems. It is to be installed at the European Space Agency’s (ESA) Optical Ground Station in Tenerife, Spain, in the frame of the ESO–ESA Research & Development collaboration. The higher laser power and its chirping system will lead to significant improvements in the sharpness of astronomical images taken with ground-based telescopes. The technology also opens the door for developments in laser satellite communication. Astronomical adaptive optics refers to systems…